Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2022
-
 BayesCap: Bayesian Identity Cap for Calibrated Uncertainty in Frozen Neural NetworksUddeshya U.*, Shyamgopal K.*, Yanbei C., Massimiliano M., Zeynep A.European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2022
BayesCap: Bayesian Identity Cap for Calibrated Uncertainty in Frozen Neural NetworksUddeshya U.*, Shyamgopal K.*, Yanbei C., Massimiliano M., Zeynep A.European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2022High-quality calibrated uncertainty estimates are crucial for numerous real-world applications, especially for deep learning-based deployed ML systems. While Bayesian deep learning techniques allow uncertainty estimation, training them with large-scale datasets is an expensive process that does not always yield models competitive with non-Bayesian counterparts. Moreover, many of the high-performing deep learning models that are already trained and deployed are non-Bayesian in nature and do not provide uncertainty estimates. To address these issues, we propose BayesCap that learns a Bayesian identity mapping for the frozen model, allowing uncertainty estimation. BayesCap is a memory-efficient method that can be trained on a small fraction of the original dataset, enhancing pretrained non-Bayesian computer vision models by providing calibrated uncertainty estimates for the predictions without (i) hampering the performance of the model and (ii) the need for expensive retraining the model from scratch. The proposed method is agnostic to various architectures and tasks. We show the efficacy of our method on a wide variety of tasks with a diverse set of architectures, including image super-resolution, deblurring, inpainting, and crucial application such as medical image translation. Moreover, we apply the derived uncertainty estimates to detect out-of-distribution samples in critical scenarios like depth estimation in autonomous driving
@article{uu_uncercyganneurips21, title = {BayesCap: Bayesian Identity Cap for Calibrated Uncertainty in Frozen Neural Networks}, author = {{Uddeshya U.*}, {Shyamgopal K.*,} {Yanbei C.,} {Massimiliano M.,} {Zeynep A.}}, year = {2022}, journal = {European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV)}, }
2021
-
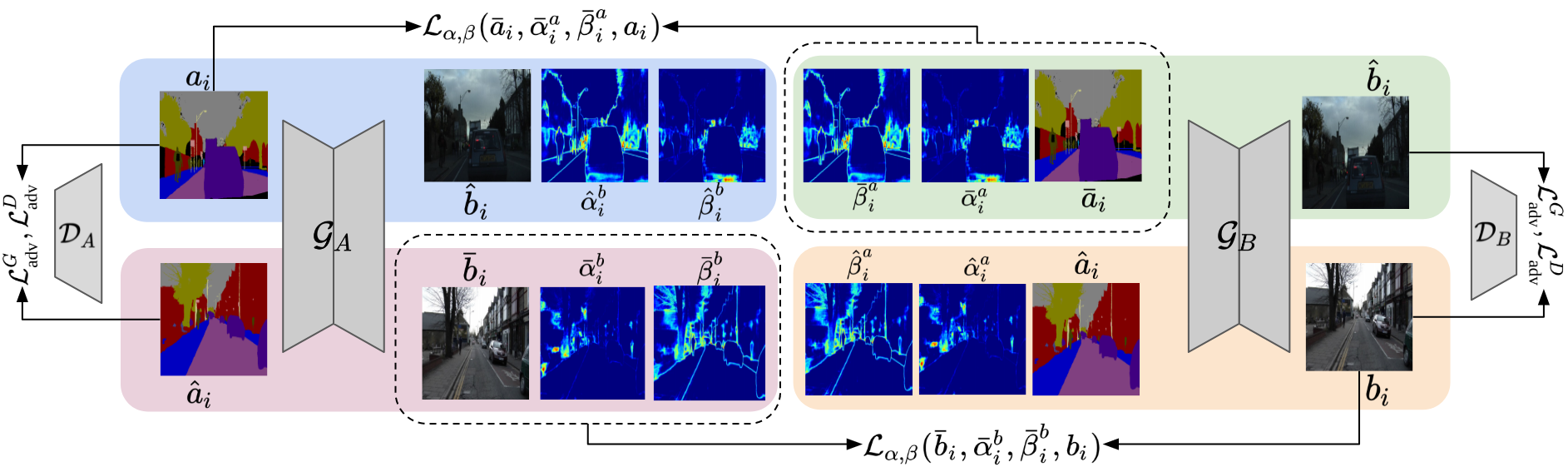 Robustness via Uncertainty-aware Cycle ConsistencyUddeshya U., Yanbei C., Zeynep A.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2021
Robustness via Uncertainty-aware Cycle ConsistencyUddeshya U., Yanbei C., Zeynep A.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2021Unpaired image-to-image translation refers to learning inter-image-domain mapping without corresponding image pairs. Existing methods learn deterministic mappings without explicitly modelling the robustness to outliers or predictive uncertainty, leading to performance degradation when encountering unseen perturbations at test time. To address this, we propose a novel probabilistic method based on Uncertainty-aware Generalized Adaptive Cycle Consistency (UGAC), which models the per-pixel residual by generalized Gaussian distribution, capable of modelling heavy-tailed distributions. We compare our model with a wide variety of state-of-the-art methods on various challenging tasks including unpaired image translation of natural images, using standard datasets, spanning autonomous driving, maps, facades, and also in medical imaging domain consisting of MRI. Experimental results demonstrate that our method exhibits stronger robustness towards unseen perturbations in test data.
@article{uu_uncercyganneurips22, title = {Robustness via Uncertainty-aware Cycle Consistency}, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Yanbei C.,} {Zeynep A.}}, year = {2021}, journal = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)}, } -
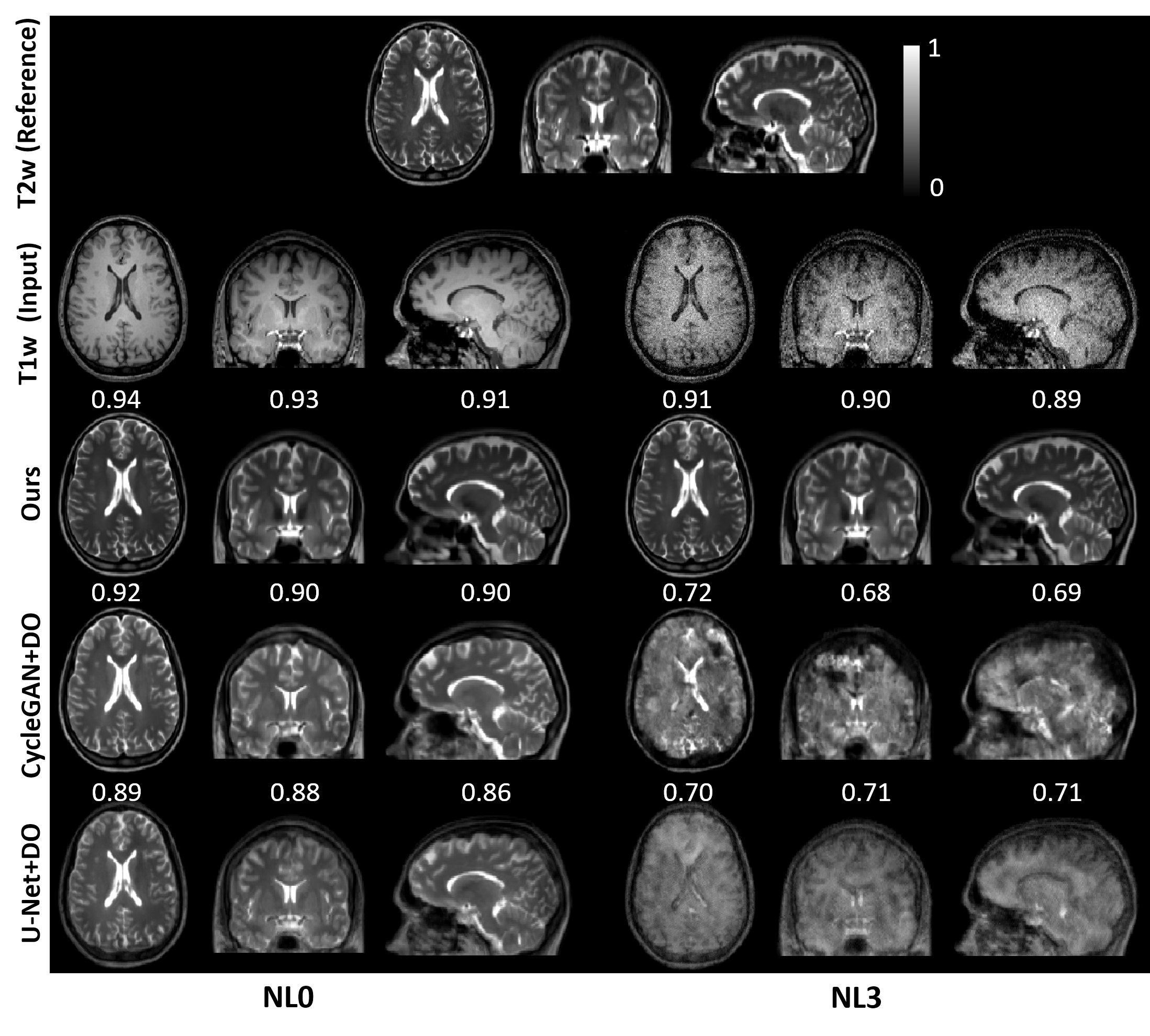 Uncertainty-aware GAN with Adaptive Loss for Robust MRI Image EnhancementUddeshya U., Viswanath P.S., Suyash P.A.ICCV workshop on CV for Automated Medical Diagnosis (ICCVw) 2021
Uncertainty-aware GAN with Adaptive Loss for Robust MRI Image EnhancementUddeshya U., Viswanath P.S., Suyash P.A.ICCV workshop on CV for Automated Medical Diagnosis (ICCVw) 2021Image-to-image translation is an ill-posed problem as unique one-to-one mapping may not exist between the source and target images. Learning-based methods proposed in this context often evaluate the performance on test data that is similar to the training data, which may be impractical. This demands robust methods that can quantify uncertainty in the prediction for making informed decisions, especially for critical areas such as medical imaging. Recent works that employ conditional generative adversarial networks (GANs) have shown improved performance in learning photo-realistic image-to-image mappings between the source and the target images. However, these methods do not focus on (i) robustness of the models to out-ofdistribution (OOD)-noisy data and (ii) uncertainty quantification. This paper proposes a GAN-based framework that (i) models an adaptive loss function for robustness to OOD-noisy data that automatically tunes the spatially varying norm for penalizing the residuals and (ii) estimates the per-voxel uncertainty in the predictions. We demonstrate our method on two key applications in medical imaging: (i) undersampled magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction (ii) MRI modality propagation. Our experiments with two different real-world datasets show that the proposed method (i) is robust to OOD-noisy test data and provides improved accuracy and (ii) quantifies voxel-level uncertainty in the predictions.
@article{uu_uncerganiccv21, title = {Uncertainty-aware GAN with Adaptive Loss for Robust MRI Image Enhancement}, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Viswanath P.S.,} {Suyash P.A.}}, year = {2021}, journal = {ICCV workshop on CV for Automated Medical Diagnosis (ICCVw)}, } -
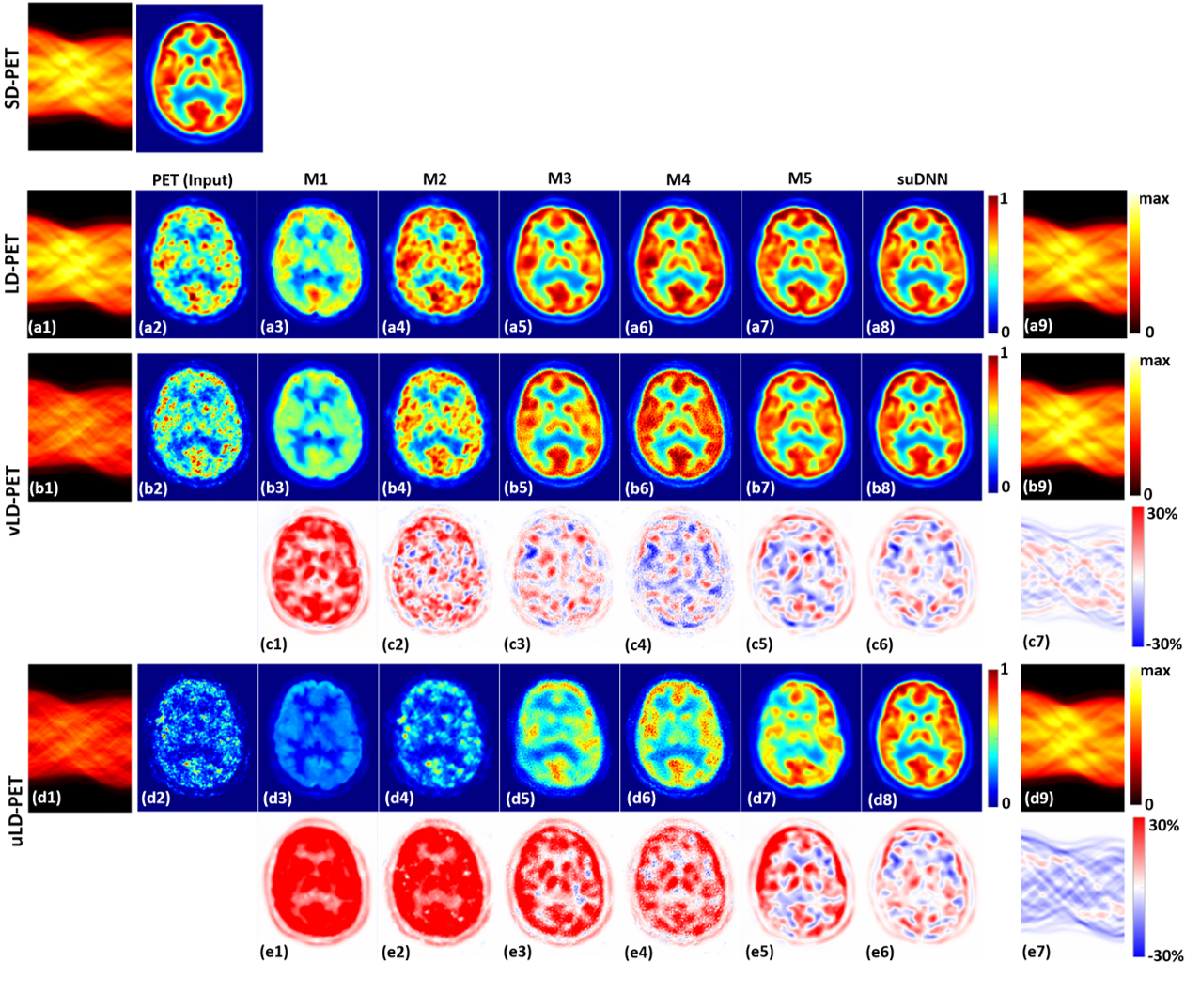 Towards Lower-Dose PET using Physics-Based Uncertainty-Aware Multimodal Learning with Robustness to Out-of-Distribution Data (*joint first author)Viswanath P.S.*, Uddeshya U.*, Gary F.E., Zhaolin C., Suyash P.A.Medical Image Analysis (MedIA) 2021
Towards Lower-Dose PET using Physics-Based Uncertainty-Aware Multimodal Learning with Robustness to Out-of-Distribution Data (*joint first author)Viswanath P.S.*, Uddeshya U.*, Gary F.E., Zhaolin C., Suyash P.A.Medical Image Analysis (MedIA) 2021Radiation exposure in positron emission tomography (PET) imaging limits its usage in the studies of radiation-sensitive populations, e.g., pregnant women, children, and adults that require longitudinal imaging. Reducing the PET radiotracer dose or acquisition time reduces photon counts, which can deteriorate image quality. Recent deep-neural-network (DNN) based methods for image-to-image translation enable the mapping of low-quality PET images (acquired using substantially reduced dose), coupled with the associated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images, to high-quality PET images. However, such DNN methods focus on applications involving test data that match the statistical characteristics of the training data very closely and give little attention to evaluating the performance of these DNNs on new out-of-distribution (OOD) acquisitions. We propose a novel DNN formulation that models the (i) underlying sinogram-based physics of the PET imaging system and (ii) the uncertainty in the DNN output through the per-voxel heteroscedasticity of the residuals between the predicted and the high-quality reference images. Our sinogram-based uncertainty-aware DNN framework, namely, suDNN, estimates a standard-dose PET image using multimodal input in the form of (i) a low-dose/low-count PET image and (ii) the corresponding multi-contrast MRI images, leading to improved robustness of suDNN to OOD acquisitions. Results on in vivo simultaneous PET-MRI, and various forms of OOD data in PET-MRI, show the benefits of suDNN over the current state of the art, quantitatively and qualitatively.
@article{uu_uncerphysmedia21, title = {Towards Lower-Dose PET using Physics-Based Uncertainty-Aware Multimodal Learning with Robustness to Out-of-Distribution Data (*joint first author)}, author = {{Viswanath P.S.*}, {Uddeshya U.*,} {Gary F.E.,} {Zhaolin C.,} {Suyash P.A.}}, year = {2021}, journal = {Medical Image Analysis (MedIA)}, } -
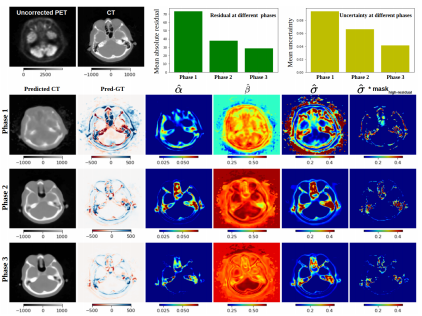 Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GANs for Medical Image TranslationUddeshya U., Yanbei C., Tobias H., Sergios G., Zeynep A.International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2021
Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GANs for Medical Image TranslationUddeshya U., Yanbei C., Tobias H., Sergios G., Zeynep A.International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2021Image-to-image translation plays a vital role in tackling various medical imaging tasks such as attenuation correction, motion correction, undersampled reconstruction, and denoising. Generative adversarial networks have been shown to achieve the state-of-the-art in generating high fidelity images for these tasks. However, the state-of-the-art GANbased frameworks do not estimate the uncertainty in the predictions made by the network that is essential for making informed medical decisions and subsequent revision by medical experts and has recently been shown to improve the performance and interpretability of the model. In this work, we propose an uncertainty-guided progressive learning scheme for image-to-image translation. By incorporating aleatoric uncertainty as attention maps for GANs trained in a progressive manner, we generate images of increasing fidelity progressively. We demonstrate the efficacy of our model on three challenging medical image translation tasks, including PET to CT translation, undersampled MRI reconstruction, and MRI motion artefact correction. Our model generalizes well in three different tasks and improves performance over state of the art under fullsupervision and weak-supervision with limited data. Code is released here: https://github.com/ExplainableML/UncerGuidedI2I
@article{uu_uncerguidedi2i, title = {Uncertainty-Guided Progressive GANs for Medical Image Translation}, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Yanbei C.,} {Tobias H.,} {Sergios G.,} {Zeynep A.}}, year = {2021}, journal = {International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI)}, }
2020
-
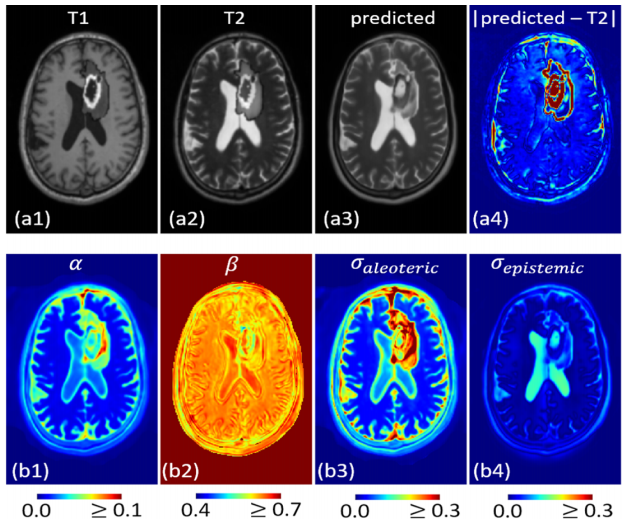 QUEST for MEDISYN: Quasi-norm based Uncertainty ESTimation for MEDical Image SYNthesisUddeshya U., Viswanath P.S., Suyash P.A.ICML Workshop on Uncertainty & Robustness in Deep Learning (ICMLw) 2020
QUEST for MEDISYN: Quasi-norm based Uncertainty ESTimation for MEDical Image SYNthesisUddeshya U., Viswanath P.S., Suyash P.A.ICML Workshop on Uncertainty & Robustness in Deep Learning (ICMLw) 2020@article{uu_icmlw1, title = {QUEST for MEDISYN: Quasi-norm based Uncertainty ESTimation for MEDical Image SYNthesis}, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Viswanath P.S.,} {Suyash P.A.}}, journal = {ICML Workshop on Uncertainty & Robustness in Deep Learning (ICMLw)}, year = {2020}, } -
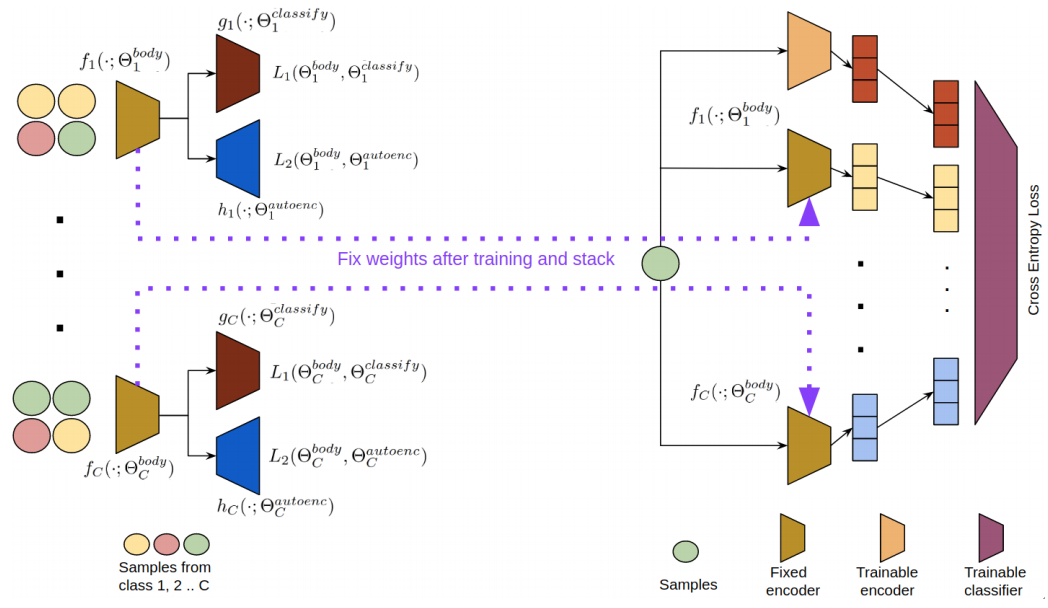 Compact Representation Learning Using Class Specific Convolution Coders-Application to Medical Image ClassificationUddeshya U., Biplap B.IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020
Compact Representation Learning Using Class Specific Convolution Coders-Application to Medical Image ClassificationUddeshya U., Biplap B.IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020Medical image classification using deep learning techniques rely on highly curated datasets, which are difficult and expensive to obtain in real world due significant expertise required to annotate the dataset. We propose a novel framework called Class Specific Convolutional Coders (CSCC) to tackle the problem of learning highly discriminative, compact and non-redundant feature space from a relatively small amount of labelled images. We design separate attention-driven convolution network based feature extractors for the categories. These feature learning modules are further intuitively combined so as to make the whole image recognition system end-to-end trainable. Results on different medical image classification tasks show the advantages of our contributions, where our proposed methods outperforms the benchmark supervised deep convolutional networks (CNNs) trained from scratch.
@article{uu_compactresl, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Biplap B.}}, title = {Compact Representation Learning Using Class Specific Convolution Coders-Application to Medical Image Classification}, year = {2020}, pages = {1266--1270}, doi = {10.1109/ISBI45749.2020.9098415}, journal = {IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI)}, }
2019
-
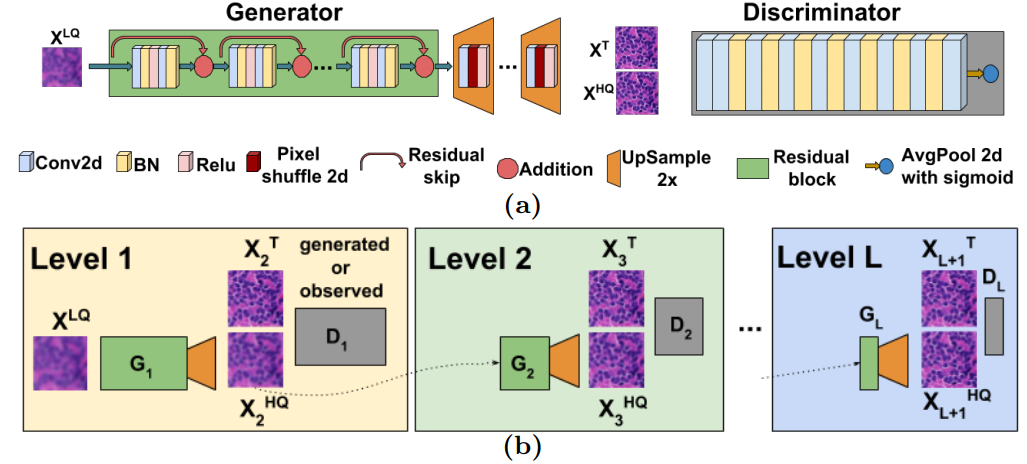 A Mixed-Supervision Multilevel GAN Framework for Image Quality EnhancementUddeshya U., Suyash P.A.International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2019
A Mixed-Supervision Multilevel GAN Framework for Image Quality EnhancementUddeshya U., Suyash P.A.International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2019Deep neural networks for image quality enhancement typically need large quantities of highly-curated training data comprising pairs of low-quality images and their corresponding high-quality images. While high-quality image acquisition is typically expensive and time-consuming, medium-quality images are faster to acquire, at lower equipment costs, and available in larger quantities. Thus, we propose a novel generative adversarial network (GAN) that can leverage training data at multiple levels of quality (e.g., high and medium quality) to improve performance while limiting costs of data curation. We apply our mixed-supervision GAN to (i) super-resolve histopathology images and (ii) enhance laparoscopy images by combining super-resolution and surgical smoke removal. Results on large clinical and pre-clinical datasets show the benefits of our mixed-supervision GAN over the state of the art.
@article{uu_qegan, title = {A Mixed-Supervision Multilevel {GAN} Framework for Image Quality Enhancement}, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Suyash P.A.}}, pages = {556--564}, year = {2019}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-32254-0\_62}, journal = {International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI)}, } -
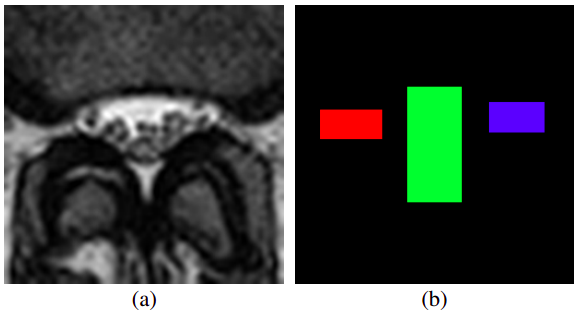 Spinal Stenosis Detection in MRI using Modular Coordinate Convolutional Attention NetworksUddeshya U., Badrinath S., Meenakshi S.IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2019
Spinal Stenosis Detection in MRI using Modular Coordinate Convolutional Attention NetworksUddeshya U., Badrinath S., Meenakshi S.IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) 2019Spinal stenosis is a condition in which a portion of spinal canal narrows and exerts pressure on nerves that travel through it causing pain and numbness that might require surgery. This narrowing can be caused by pathologies in bony structures (vertebrae) or soft tissue structures (intervertebral discs) that comprise the spine. Radiography, particularly Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the modality of choice to evaluate stenosis and intervertebral disc pathology. Radiologists examine axial MRI scans at various levels along the spine to detect stenosis. Further, they evaluate the diameters of spinal canal and bulging in nearby discs which can indicate narrowing and compression on nerves. Hence measuring various diameters in a scan is a crucial step in diagnosis. However, affected regions occupy a very small fraction of the scan and there is virtually no room for error as a deviation of few pixels will also lead to discrepancies in measured and original lengths which makes it a very difficult and laborious task to measure the length of such intricate structures accurately. We propose a novel deep learning based solution to tackle this problem. Our method attempts to solve it in two independent modules and allows us to make prediction on the enlarged section of the scan which also makes it easier to measure various lengths. Human radiologists focus on certain parts of the scan rather than attending to the entire scan which largely consists of irrelevant background. We design our modular approach to mimic this attention mechanism. Both of our modules are built using coordinate convolutional networks, we also perform the comparison with baseline and empirically demonstrate superiority of our approach.
@article{uu_spindlemri, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Badrinath S.,} {Meenakshi S.}}, title = {Spinal Stenosis Detection in MRI using Modular Coordinate Convolutional Attention Networks}, year = {2019}, pages = {1--8}, doi = {10.1109/IJCNN.2019.8852085}, journal = {IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)}, } -
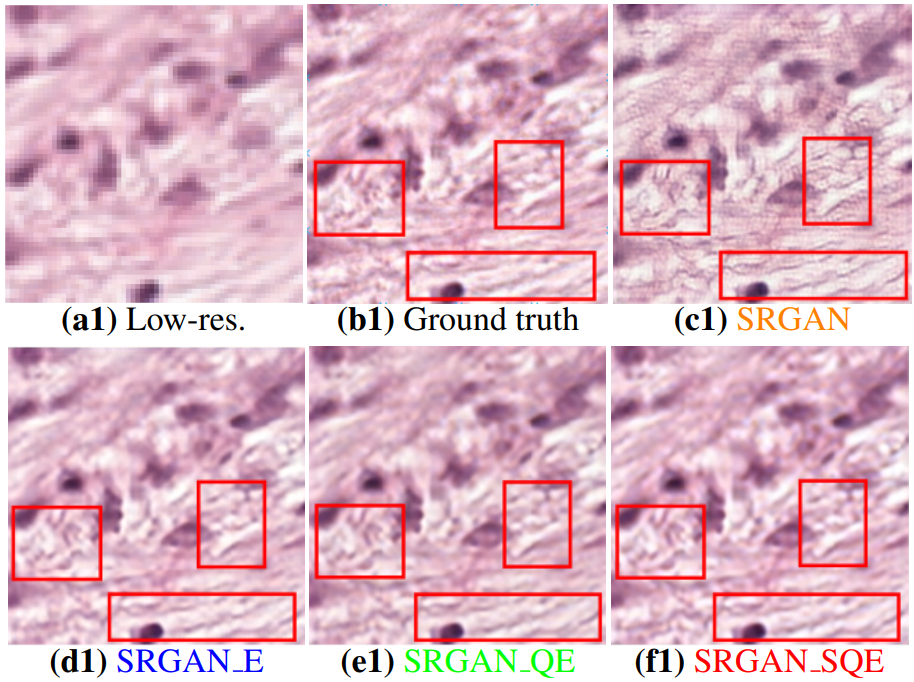 Robust Super-Resolution GAN, with Manifold-Based and Perception LossUddeshya U., Suyash P.A.IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2019
Robust Super-Resolution GAN, with Manifold-Based and Perception LossUddeshya U., Suyash P.A.IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2019Super-resolution using deep neural networks typically relies on highly curated training sets that are often unavailable in clinical deployment scenarios. Using loss functions that assume Gaussian-distributed residuals makes the learning sensitive to corruptions in clinical training sets. We propose novel loss functions that are robust to corruptions in training sets by modeling heavy-tailed non-Gaussian distributions on the residuals. We propose a loss based on an autoencoder-based manifold-distance between the super-resolved and high-resolution images, to reproduce realistic textural content in super-resolved images. We propose to learn to super-resolve images to match human perceptions of structure, luminance, and contrast. Results on a large clinical dataset shows the advantages of each of our contributions, where our framework improves over the state of the art.
@article{uu_rsrgan, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Suyash P.A.}}, title = {Robust Super-Resolution GAN, with Manifold-Based and Perception Loss}, year = {2019}, pages = {1372-1376}, doi = {10.1109/ISBI.2019.8759375}, journal = {IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI)}, } -
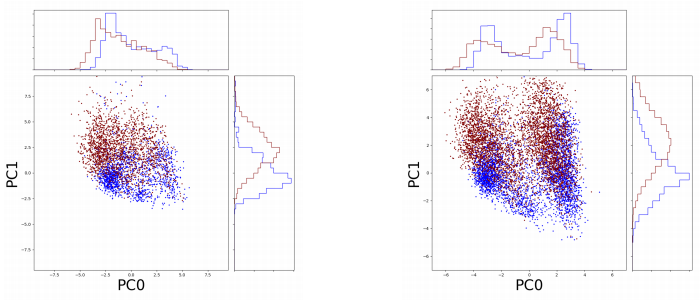 Removal of Batch Effects using GANsUddeshya U., Arjun J.2019
Removal of Batch Effects using GANsUddeshya U., Arjun J.2019Many biological data analysis processes like Cytometry or Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) produce massive amounts of data which needs to be processed in batches for down-stream analysis. Such datasets are prone to technical variations due to difference in handling the batches possibly at different times, by different experimenters or under other different conditions. This adds variation to the batches coming from the same source sample. These variations are known as Batch Effects. It is possible that these variations and natural variations due to biology confound but such situations can be avoided by performing experiments in a carefully planned manner. Batch effects can hamper downstream analysis and may also cause results to be inconclusive. Thus, it is essential to correct for these effects. This can be solved using a novel Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) based framework that is proposed here, advantage of using this framework over other prior approaches is that here it is not required to choose a reproducing kernel and define its parameters. Results of the framework on a mass cytometry dataset are reported.
@article{uu_rbatch, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Arjun J.}}, title = {Removal of Batch Effects using GANs}, year = {2019}, } -
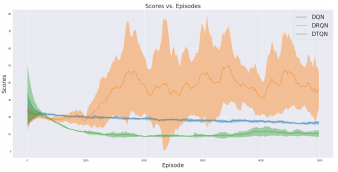 Transformer based Reinforcement Learning for GamesUddeshya U., Nikunj S., Suchetha R., Mayanka M.2019
Transformer based Reinforcement Learning for GamesUddeshya U., Nikunj S., Suchetha R., Mayanka M.2019Recent times have witnessed sharp improvements in reinforcement learning tasks using deep reinforcement learning techniques like Deep Q Networks, Policy Gradients, Actor Critic methods which are based on deep learning based models and back-propagation of gradients to train such models. An active area of research in reinforcement learning is about training agents to play complex video games, which so far has been something accomplished only by human intelligence. Some state of the art performances in video game playing using deep reinforcement learning are obtained by processing the sequence of frames from video games, passing them through a convolutional network to obtain features and then using recurrent neural networks to figure out the action leading to optimal rewards. The recurrent neural network will learn to extract the meaningful signal out of the sequence of such features. In this work, we propose a method utilizing transformer networks which have recently replaced RNNs in Natural Language Processing (NLP), and perform experiments to compare with existing methods.
@article{uu_trl, author = {{Uddeshya U.}, {Nikunj S.,} {Suchetha R.,} {Mayanka M.}}, title = {Transformer based Reinforcement Learning for Games}, year = {2019}, }